K8S Notes
Bookmark this to keep an eye on my K8s notes updates!
Project maintained by kevinsulatra Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Kubernetes Architecture
- Kubernetes Cluster Overview:
- Kubernetes is commonly utilized as a cluster, distributed across multiple servers to handle diverse tasks and distribute system loads.
- Designed to meet Google’s requirements, where billions of containers start weekly.
- Boasts high horizontal scalability, enabling clusters with thousands of server nodes across various datacenters and regions.
- Kubernetes Cluster Components:
- Control Plane Node(s):
- Considered the brains of the operation.
- Houses various components responsible for managing the cluster, overseeing tasks such as deployment, scheduling, and self-healing of containerized workloads.
- Worker Nodes:
- Dedicated to running applications in the cluster.
- Sole responsibility is executing applications, lacking additional logic.
- Behavior, such as initiating a container, is entirely controlled by the control plane node.
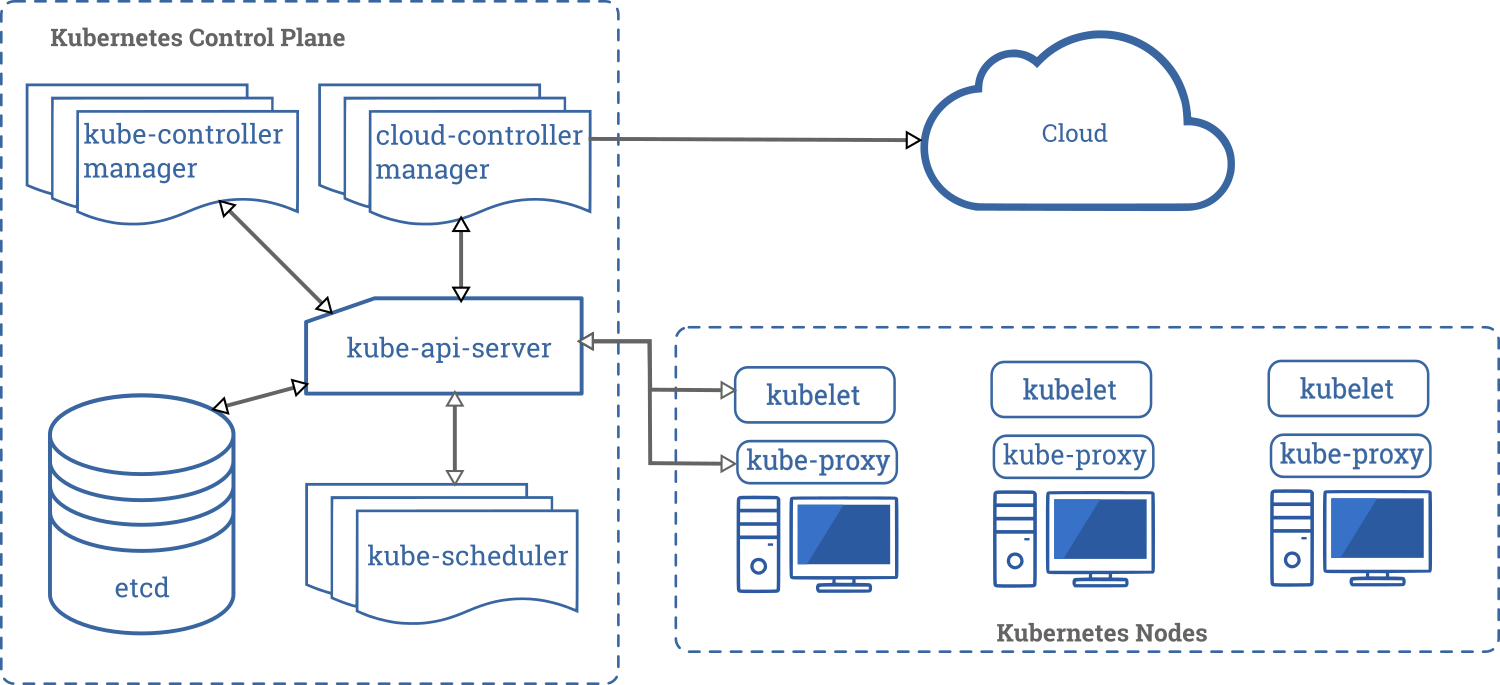 Kubernetes Architecture
Kubernetes Architecture
- Control Plane Node(s):
Control plane nodes in a Kubernetes cluster typically host the following services:
- API Server:
- Serves as the front-end for the Kubernetes control plane.
- Validates and processes RESTful API requests, initiating corresponding actions within the cluster.
- etcd:
- Consistent and highly-available key-value store used as Kubernetes’ primary data store.
- Stores configuration data, ensuring that the entire cluster maintains a consistent state.
- Scheduler:
- Watches for newly created Pods with no assigned node and selects a node for them to run on.
- Considers factors such as resource availability, affinity/anti-affinity specifications, and constraints.
- Controller Manager:
- Runs controller processes, responsible for observing the state of the cluster and making necessary changes to achieve the desired state.
- Examples include the replication controller, endpoint controller, and namespace controller.
- Cloud Controller Manager (Optional):
- Communicates with the underlying cloud provider’s API to manage resources in the cloud (e.g., load balancers or storage).
- Specific to cloud-based Kubernetes deployments and is optional based on the environment.
Worker nodes in a Kubernetes cluster typically consist of the following components:
- Kubelet:
- The primary agent running on each worker node.
- Responsible for ensuring that containers within Pods are running and healthy.
- Communicates with the control plane to receive instructions and report the status of its assigned node.
- Container Runtime:
- The software responsible for running containers, such as Docker, containerd, or cri-o.
- Implements the Container Runtime Interface (CRI) to interface with the Kubelet.
- Kube Proxy:
- Maintains network rules on nodes, enabling communication between Pods and external traffic.
- Implements the Kubernetes Service abstraction, ensuring load balancing and network proxying.
- Pods:
- Basic building blocks of a Kubernetes application.
- Containers within a Pod share the same network namespace, enabling them to communicate easily.
- cAdvisor (Optional):
- Stands for Container Advisor.
- Collects, aggregates, processes, and exports information about running containers.
- Optional, but can be used for monitoring and performance analysis.
These components collectively form the worker node, responsible for executing applications and running containers as directed by the control plane.
- Kubernetes Design Resilience:
- Kubernetes’ design allows applications on a worker node to persist even if the control plane is unavailable.
- Existing applications continue to run, ensuring ongoing operation, although certain functionalities (e.g., scaling, scheduling new applications) are hindered during control plane downtime.
- Kubernetes Namespace Concept:
- Not Kernel Namespaces:
- Kubernetes namespaces differ from kernel namespaces used to isolate containers.
- Virtual Clusters for Multi-Tenancy:
- Kubernetes namespaces divide a cluster into multiple virtual clusters.
- Useful for multi-tenancy scenarios where multiple teams share a cluster.
- Limited Isolation:
- Important to note that Kubernetes namespaces don’t provide strong isolation.
- Analogous to a directory on a computer, allowing organization and user access management.
- Should be viewed as a means to organize objects and control user access within a cluster.
- Not Kernel Namespaces: