K8S Notes
Bookmark this to keep an eye on my K8s notes updates!
Project maintained by kevinsulatra Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
K8s API
- Importance of Kubernetes API:
- The Kubernetes API stands as the most critical component in a Kubernetes cluster.
- Essential for communication with the cluster; every user and cluster component relies on the API server.
- Processing Requests in Kubernetes API:
- Authentication:
- Users or components must present a means of identity for authentication.
- Commonly accomplished with a digitally signed certificate (X.509) or an external identity management system.
- Kubernetes users are externally managed, and technical users can be authenticated using Service Accounts.
- Authorization:
- Decides the permissions granted to the requester.
- Implemented in Kubernetes through Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
- Admission Control:
- In the final step, admission controllers can modify or validate the request.
- Example: An admission controller could block a request to use a container image from an untrustworthy registry.
- External tools like Open Policy Agent can manage admission control.
- Authentication:
- Kubernetes API Implementation:
- Implemented as a RESTful interface exposed over HTTPS.
- Through the API, users or services can create, modify, delete, or retrieve resources within the Kubernetes cluster.
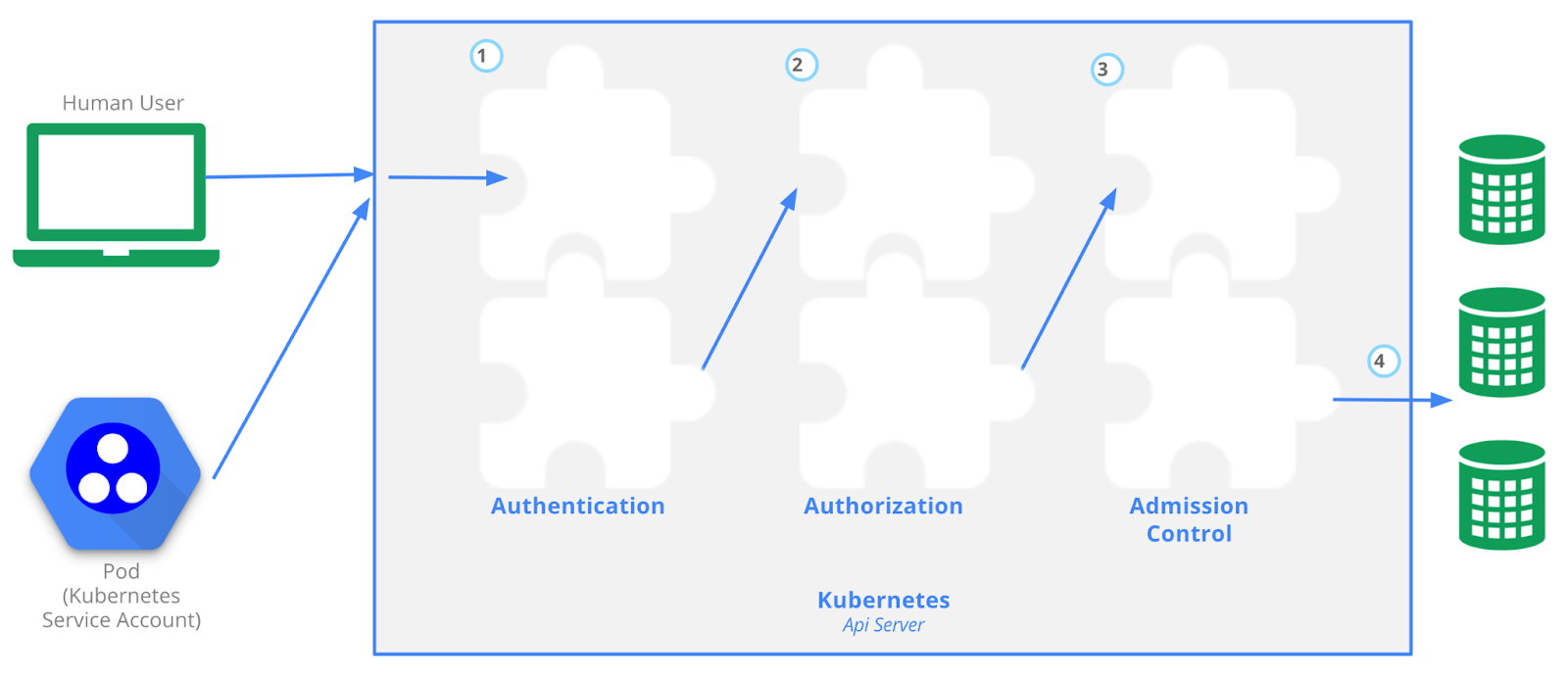 Access Control Overview, retrieved from the Kubernetes documentation
Access Control Overview, retrieved from the Kubernetes documentation